검색결과 리스트
분류 전체보기에 해당되는 글 12건
- 2020.10.11 [안드로이드] TTS (TextToSpeech) 예제
- 2020.09.14 [Kotlin] DataClass
- 2020.09.13 [Kotlin] 클래스 정리
- 2020.09.13 [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when
- 2020.09.13 [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링
- 2020.09.13 [Kotlin] Array 배열
- 2020.09.13 [Kotlin] String 문자열
- 2020.08.02 [iOS] - UITextView
- 2020.08.02 [iOS] - UILabel
- 2020.08.01 [iOS] - SnapKit : Layout 정리
- 2020.08.01 [iOS] - CocoaPods(코코아팟), Xcode의 Library 관리
- 2020.07.31 [iOS] - Storyboard와 SwiftUI 없이 Project 만들기
글
[안드로이드] TTS (TextToSpeech) 예제
1. TTS Class 소스 (커스텀)
class TTS_Module {
companion object : TextToSpeech.OnInitListener {
private const val TTS_DATA_CHECK_CODE = 7200
private var ctx : Activity? = null
private var TTS: TextToSpeech? = null
private var text: String = ""
private var locale: Locale = Locale.KOREA
private var level: Float = PITCH.NOMAL.level
private var speed: Float = SPEED.s1_0X.speed
fun toSpeech(ctx: Activity, text: String ,
locale: Locale? = Locale.KOREA,
level: Float = PITCH.NOMAL.level,
speed: Float = SPEED.s1_0X.speed){
this.text = text
this.ctx = ctx
if (locale != null) this.locale = locale
if (level != null) this.level = level
if (speed != null) this.speed = speed
if(TTS == null) {
val intent = Intent()
intent.action = TextToSpeech.Engine.ACTION_CHECK_TTS_DATA
ctx.startActivityForResult(intent, TTS_DATA_CHECK_CODE)
}else{
speeach()
}
}
private fun speeach(){
setLanguage(this.locale)
setPitch(this.level)
setSpeechRate(this.speed)
// 블루투스 연결시 패이드인으로 앞에 소리가 살짝 끊김을 해소 하기 위해
// 무은 MP3 를 재생 후 TTS 작동. (MP3는 0.5~1초 정도가 적당해 보임)
val resID: Int = ctx!!.resources.getIdentifier(
"no_sound", "raw", ctx!!.packageName)
val player: MediaPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(ctx, resID)
player.setOnCompletionListener {
Log.d("B-Rain", "TTS 시작")
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT > Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
TTS!!.speak("", TextToSpeech.QUEUE_FLUSH, null, null)
TTS!!.speak(text, TextToSpeech.QUEUE_ADD, null, null)
} else {
TTS!!.speak("", TextToSpeech.QUEUE_FLUSH, null)
TTS!!.speak(text, TextToSpeech.QUEUE_ADD, null)
}
}
player.start()
Log.d("B-Rain", "무음 MP3 시작")
}
override fun onInit(status: Int) {
if (status == TextToSpeech.SUCCESS) {
if (TTS!!.isLanguageAvailable(Locale.KOREA) >=
TextToSpeech.LANG_AVAILABLE) {
TTS!!.language = Locale.KOREA
speeach()
}
}
}
/** 음성 언어 */
fun setLanguage(locale: Locale? = Locale.KOREA) {
if (TTS != null) TTS!!.language = locale
}
/** 음성 속도 */
fun setSpeechRate(speed: Float = SPEED.s1_0X.speed) {
if (TTS != null) TTS!!.setSpeechRate(speed)
}
/** 음성 톤 */
fun setPitch(level: Float = PITCH.NOMAL.level) {
if (TTS != null) TTS!!.setPitch(level)
}
fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) {
if (requestCode === TTS_DATA_CHECK_CODE) {
if (resultCode === TextToSpeech.Engine.CHECK_VOICE_DATA_PASS) {
if(TTS == null) {
TTS = TextToSpeech(ctx, this)
}else{
speeach()
}
} else {
val installIntent = Intent()
installIntent.action =
TextToSpeech.Engine.ACTION_INSTALL_TTS_DATA
ctx!!.startActivity(installIntent)
}
}
}
fun onPause() {
if (TTS != null) {
if (TTS!!.isSpeaking) {
TTS!!.stop()
}
}
}
fun onDestroy() {
if (TTS != null) {
if(TTS!!.isSpeaking) {
TTS!!.stop();
}
TTS!!.shutdown();
}
}
}
}
enum class PITCH {
ROW {
override fun index() = 1
override val level: Float
get() = 0.1F
},
NOMAL {
override fun index() = 2
override val level: Float
get() = 1.0F
},
HIGH {
override fun index() = 3
override val level: Float
get() = 2.0F
};
abstract fun index() : Int
abstract val level : Float
}
enum class SPEED {
ZERO {
override fun index() = 1
override val speed: Float
get() = 0.1F
},
s1_0X {
override fun index() = 2
override val speed: Float
get() = 1.0F
},
s1_5X {
override fun index() = 3
override val speed: Float
get() = 1.5F
},
s2_0X {
override fun index() = 4
override val speed: Float
get() = 2.0F
};
abstract fun index() : Int
abstract val speed : Float
}2. 사용법
- Base Activity로 만들어서 상속 시켜 사용 하면 적당 할 듯.
class BaseActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
btn_tts.setOnClickListener {
// TTS_Module 실행 (SingleTone Clas)
TTS_Module.toSpeech(
this,
"TTS 출력 시킴"
,Locale.KOREA // 옵션
,PITCH.NOMAL.level // 옵션
,SPEED.s1_0X.speed // 옵션
)
}
}
override fun onActivityResult(requestCode: Int, resultCode: Int, data: Intent?) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data)
// TTS 데이터 가 없을 경우 "TTS_Module" 클래스가 처리 할 수 있도록 전달
TTS_Module.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data)
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
// Pause 일 때
TTS_Module.onPause()
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
// Destroy 일 때
TTS_Module.onDestroy();
}
}
'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] DataClass (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] Array 배열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[Kotlin] DataClass
1. 데이터 클래스 기능
equals()
hashCode()
toString()
componentN()
copy()
data class Book(
var name: String,
var authorName: String = "dudu",
var lastModified: Long = 1234567,
var rating: Float = 5f,
var downloads: Int = 1000
)
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var book = Book("Android tutorials","Hup..", 1234567, 4.5f, 1000)
book = Book("Kotlin")
book = Book("Swift",downloads = 500)
book = Book("Java","zzz",rating = 5f, downloads = 1000)
book = Book("Python","YYY",rating = 5f)
println(book.toString())
val newBook = book.copy(name = "iOS dev")
println("Hashcode is ${newBook.hashCode()}")
if(!newBook.equals(book))
println("newBook and book are NOT equal")
println(book.component1()) //Python
println(book.component2()) //YYY
println(book.component3()) //1234567
println(book.component4()) //5f
println(book.component5()) //1000
}
// 변수 이름을 사용하면 원하는 값만 선택적으로 입력 가능 하다.
// toString()함수는 클래스의 값을 출력 한다.
// copy() 는 원하는 값만 변경하여 새로운 val 객채를 만들 수 있다.
// hashCode() 헤시코드를 반환 함.
// equals() " == " 과 같음.
// omponent(n) 생성자에 명시된 순서(n)에 맞는 개체로 접근
2. Destructuring
data class Book(val name: String, val authorName: String = "kaka", val lastModified: Long = 1234567, val rating: Float = 5f, val downloads: Int = 1000)
val book = Book("Android tutorials","dudu", 1234567, 4.5f, 1000)
val (n,a,date,rating,downloads) = book
==>
n = "Android tutorials"
a = "dudu"
date = 1234566
rating = 4.5f
downloads = 1000equals()
hashCode()
toString()
componentN()
copy()
'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [안드로이드] TTS (TextToSpeech) 예제 (0) | 2020.10.11 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] Array 배열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[Kotlin] 클래스 정리
Class 기본 사용
class User {
var loggedIn: Boolean = false
val cantChangeValue = "Hi"
fun logOn() {
loggedIn = true
}
fun logOff() {
loggedIn = false
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val user = User()
println(user.loggedIn) //false
user.logOn()
println(user.loggedIn) //true
user.logOff()
println(user.loggedIn) //false
user.cantChangeValue = "Hey" //won't compile. Can't modify a final variable.
}Class 생성자 "init"
예 1.) =============================
class MultiInit(name: String) {
init {
println("First initializer block that prints ${name}")
}
init {
println("Second initializer block that prints ${name.length}")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var multiInit = MultiInit("Kotlin")
}
출력>>>>>>>
I/System.out: First initializer block that prints Kotlin
I/System.out: Second initializer block that prints 6
예 2.) ========= With "also"===========
class MultiInit(name: String) {
val firstProperty = "First property: $name".also(::println)
init {
println("First initializer block that prints ${name}")
}
val secondProperty = "Second property: ${name.length}".also(::println)
init {
println("Second initializer block that prints ${name.length}")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var multiInit = MultiInit("Kotlin")
}
출력>>>>>>>
I/System.out: First property: Kotlin
I/System.out: First initializer block that prints Kotlin
I/System.out: Second property: 6
I/System.out: Second initializer block that prints 6Class 보조 생성자 "constructor"
class Student {
var name: String
val age : Int
constructor(name: String, age: Int)
{
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
fun printDetails()
{
println("Name is $name and Age is $age")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var student = Student("gugu", 17)
student.printDetails()
}
출력 >>>>>>>>
//Name is gugu and Age is 17init + constructor
class Student(var name: String, val age: Int) {
var skill: String
init {
skill = "play"
}
constructor(name: String, age: Int, skill: String) : this(name, age) {
this.skill = skill
}
fun printDetails() {
if (skill.equals("play"))
println("Name is $name and Age is $age")
else
println("Name is $name and Age is $age Skill is $skill")
}
}
I/System.out: Name is no-b-rain and Age is 1
I/System.out: Name is dudu and Age is 20 Skill is dodory
생성자의 인수 , 인수의 기본값 설정
예 1.)
class User(name: String, val isAdmin: Boolean) {
var username = name //username = name
val _isAdmin = isAdmin //_isAdmin = isAdmin
init {
username= username + "https://no-b-rain.tistory.com/"
println("Author Name is $name. Is Admin? $_isAdmin")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var user = User("no-b-rain",false)
// Error Code : user.isAdmin = true //won't compile since isAdmin is val
// Error Code : user._isAdmin = true //won't compile. Same reason.
user = User("no-Brain",true)
}
예 2.)
class User(name: String, var website: String = "no-b-rain") {
init {
println("Author $name writes at $website")
}
init {
website = website + ".com"
println("Author $name writes at $website")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var user = User("no-b-rain","dudu")
user = User("no-Brain","dudu")
}
I/System.out: Author no-b-rain writes at dudu
I/System.out: Author no-b-rain writes at dudu.com
I/System.out: Author no-Brain writes at dudu
I/System.out: Author no-Brain writes at dudu.com
커스텀 setter , getter
class Name{
var post: String = "default"
set(value) {if(!post.isNotEmpty()) {
throw IllegalArgumentException(" Enter a valid name")
}
field = value
}
get() {
return field.capitalize()
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
var name = Name()
name.post = "kotlin classes"
println(name.post)
name.post = "kotlin data Classes our next Tutorial"
println(name.post)
}abstract
abstract class Person(name: String) {
init {
println("Abstract Class. init block. Person name is $name")
}
abstract fun displayAge()
}
class Teacher(name: String): Person(name) {
var age : Int
init {
age = 24
}
override fun displayAge() {
println("Non-abstract class displayAge function overridden. Age is $age")
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val person = Teacher("Anupam")
person.displayAge()
}
//Following is printed in the console.
//Abstract Class. init block. Person name is Anupam
//Non-abstract class. Age is 24'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [안드로이드] TTS (TextToSpeech) 예제 (0) | 2020.10.11 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] DataClass (0) | 2020.09.14 |
| [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] Array 배열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when
for in
예 1.) ===============================================
for (i in 0..5) {
print(i)
}
예 2.) ===============================================
val items = listOf(10, 20, 30, 40)
for (i in items)
println("value is $i")
//Following is printed to the console.
value is 10
value is 20
value is 30
value is 40
예 3. index 출력 "indices" ============================
val items = listOf(10, 20, 30, 40)
for (i in items.indices)
println("value is $i")
//Following is printed to the console:
value is 0
value is 1
value is 2
value is 3
예 4.) index 와 element 출력 "withIndex()" =============
val items = listOf(10, 20, 30, 40)
for ((i,e) in items.withIndex())
println("the index is $i and the element is $e")
//Following is printed on the console:
the index is 0 and the element is 10
the index is 1 and the element is 20
the index is 2 and the element is 30
the index is 3 and the element is 40
forEach [ Range " .. 연산자 " ]
(2..5).forEach{
println(it)
}
//or
(2..5).forEach{
i -> println(i)
}
//Following is printed on the console:
2
3
4
5
존재 여부 " in , !in"
var x = 5
if(x in 1..10)
{
print("x exists in range") //this gets printed
}
else{
print("x does not exist in range")
}
x = 15
if(x !in 1..10)
{
print("x does not exist in range") //this gets printed
}
else{
print("x does exist in range")
}
Range ..는 역순으로 사용할 수 없음. --> 10..0 처럼 거꾸로 사용 못함.
여기에서 downTo키워드를 사용
var x = 5
if(x in 10 downTo 1)
{
print("x exists in range") //this gets printed
}
else{
print("x does not exist in range")
}
for (i in 5 downTo 0)
print(i) //543210마지막 요소를 제외 "until"
for (i in 1 until 4) {
print(i)
}
//prints 123단계적으로 범위를 탐색 "step"
for (i in 1..5 step 3) print(i) // prints 14
for (i in 4 downTo 1 step 2) print(i) // prints 42N번 반복 실행 "repeat"
repeat(3) {
println("Hello World!")
println("Kotlin Control Flow")
}선택, 분기분 "when"
예 1.)
var num = 10
when (num) {
0 -> print("value is 0")
5 -> print("value is 5")
else -> {
print("value is neither 0 nor 5") //this gets printed.
}
}
예 2.) until
var valueLessThan100 = when(101){
in 1 until 101 -> true
else -> {
false
}
}
print(valueLessThan100) //false
제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when
'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] DataClass (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] Array 배열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] String 문자열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링
Let function은 아래와 같이 참조가 nullable이 아닌 경우에만 지정된 람다 함수를 실행
newString = " Kotlin from Android"
newString?.let { println("The string value is: $it") }
newString = null
newString?.let { println("The string value is: $it") }also 사용
var c = "Hello"
var newString = "chenge string."
newString?.let { c = it }.also {
println("Logging the value: $it")
}
Log.d("TAG",c)
--> "chenge string."Elvis 연산자 : Elvis 연산자를 ?:사용하면 아래와 같이 null 대신 기본값을 설정할 수 있다.
var newString : String? = "JournalDev.com"
println(newString?.length) //prints 14
newString = null
println(newString?.length?:"-1") //prints -1Null value filter
var array2: Array<Any?> = arrayOf("1", "2", "3", null)
var newArray = array2.filterNotNull()
println(newArray.size) //prints
'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] DataClass (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] Array 배열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] String 문자열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[Kotlin] Array 배열
배열 기본 선언
val abcArray = arrayOf("A","B","C","D","E")
val tmpArray = arrayOf("A",1,1L,1.2,false)배열 접근
val array1 = arrayOf(1,2,3,4)
val array3 = arrayOf<Long>(1,2,3,4)
array3.get(0)
array3[0]
array1[1] = 6
array1.set(1,6)
println("Size is ${array1.size}") //Size is 4배열 특정 로직 반복
val array = Array(6) {i-> "Hi "+i}
for(element in array)
println(element)
//prints the following in the console
Hi 0
Hi 1
Hi 2
Hi 3
Hi 4
Hi 5배열 반전 반환
var array1 = arrayOf(1,2,3,4)
array1 = array1.reversedArray()
for(element in array1)
{
println(element)
}
//Prints 4,3,2,1배열 반전 - 변수 자체 반전 변경
var array1 = arrayOf(1,2,3,4)
array1.reverse()
for(element in array1)
{
println(element)
}
//prints 4,3,2,1배열 합
var array1 = arrayOf(1,2,3,4)
println(array1.sum()) //prints 10배열 추가
var array1 = arrayOf(1,2,3,4)
array1 = array1.plus(5)
//or
array1 = array1.plusElement(5)
for(element in array1)
{
println(element)
}
//prints 1,2,3,4,5배열 값 체우기( 범위 지정 )
var array1 = arrayOf(1,2,3,4)
array1.fill(0,0,array1.size)
for(element in array1)
{
println(element)
}
//prints 0,0,0,0,0배열에 배열 추가
var oldArray = Array(6, {i->i*10})
array1.fill(0,0,array1.size)
array1 = array1.plus(oldArray)
for(element in array1)
{
println(element)
}
'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] DataClass (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] String 문자열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[Kotlin] String 문자열
문자열 기본
var str: String = "Hello"
//or
var str = "Hello"
var newString: String = 'A' //ERROR
var newString: String = 2 //ERROR문자열 합치기 기본
var str = "Hello"
str += "Kotlin Strings"빈문자열
var s = String() //creates an empty string.문자열 길이
val str = "Hello Kotlin Strings"
println(str.length) //prints 20특정 위치 문자 반환
val str = "Hello Kotlin Strings"
println(str.get(0)) //print 'H'
println(str.subSequence(0,5)) //prints Hell
문자열 비교
var str = "Hello Kotlin Strings"
var s = String()
s = "Hello KOTLIN Strings"
println(s.compareTo(str)) //prints -32
println(s.compareTo(str,true)) //prints 0문자열 이스케이프 문자
- \n 개행.
- \r 캐리지 리턴.
- \t 탭.
- \b 역행 키이
- \" 큰 따옴표
- \' 작은 따옴표
- \\ 백 슬래시
- \$ 달러 – 문자열 주입
var len = str.length
var newStr = "Length of str is ${str.length}"
//or
var newStr = "Length of str is $len"
println(Length of str is ${str.length})Raw 문자열 (여러줄)
var rawString = """Hi How you're Doing
I'm doing fine\n.
I owe you $5.50"""
print(rawString)
//prints the following
Hi How you're Doing
I'm doing fine\n. /** \n 은 소용 없음. **/
I owe you $5.50Raw 문자열 (여러줄) - 줄바꿈
var rawString = """Hi How you're Doing
|I'm doing fine.
|I owe you $5.50""".trimMargin("|")
print(rawString)
//Prints the following to the console.
Hi How you're Doing
I'm doing fine.
I owe you $5.50String override
class Student(var name: String, var age: Int)
{
override fun toString(): String {
return "Student name is $name and age is $age"
}
}
//The following code is written inside the main function of the Kotlin class.
var student = Student("Banana", 16)
print(student) //prints Student name is Banana and age is 16비교 연산
- Reference Equality === : 두 개체의 포인터가 동일한 지 확인
- Structural Equality == : 두 객체의 내용이 동일한 지 확인
'Android (Kotlin)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] DataClass (0) | 2020.09.14 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] 클래스 정리 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] 제어문 for , forEach , range , repeat , when (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] let 과 also , Elvis 연산자 와 Null 값 필터링 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
| [Kotlin] Array 배열 (0) | 2020.09.13 |
글
[iOS] - UITextView
- UITextView 내용 정리
- Snapkit으로 ui-component들을 배치합니다.
- SnapKit의 기본 지식은 2020/08/01 - [iOS] - iOS - SnapKit : Layout 정리를 참고.
import Foundation
import SnapKit
class TestUITextViewVC: UIViewController {
lazy var noB_TextView : UITextView = {
let value : UITextView = UITextView()
value.backgroundColor = UIColor.cyan
value.text = "안녕하세요 No.B.Rain 입니다.
지금 여기는
https://no-b-rain.tistory.com/ 입니다."
value.textColor = UIColor.red
// 그림자를 넣고 싶다면 아래와 같이 농도를 설정
value.layer.shadowOpacity = 0.5
// Text 정렬 (왼쪽)
value.textAlignment = NSTextAlignment.left
value.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: CGFloat(20))
//UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: UIFont.buttonFontSize)
//UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: UIFont.systemFontSize)
//UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: UIFont.systemFontSize)
//UIFont.italicSystemFont(ofSize: UIFont.systemFontSize)
value.layer.masksToBounds = true
//value.layer.cornerRadius = "높이" * 0.05
//(둥근 모서리는 생성될 때 높이 값을 주입해서 설정)
// 테두리 설정
value.layer.borderWidth = 1
value.layer.borderColor = UIColor.black.cgColor
// 자동 URL 유형 처리
value.dataDetectorTypes = UIDataDetectorTypes.all
//UIDataDetectorTypes.address
//UIDataDetectorTypes.calendarEvent
//UIDataDetectorTypes.phoneNumber
//UIDataDetectorTypes.link
//UIDataDetectorTypes.flightNumber
// 편집 모드에서는 위의 "자동 URL 유형 처리" 기능이 동작하지 않음.
value.isEditable = false
return value
}()
lazy var noB_Label : UILabel = {
// Label 생성 => 가로 300 , 세로 300
let value : UILabel = UILabel (frame : CGRect (x: 0 , y: 0 , width: 300 , height: 100 ))
value.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
value.text = "No.B.Rain 노비의 문서"
value.textColor = UIColor.yellow
// Text 정렬 (중앙)
value.textAlignment = NSTextAlignment.center
// 둥근 모서리 => 둥근 모서리는 컨탠츠 높이의 5%가 가장 적당하고 이쁨(개인적으로..)
value.layer.masksToBounds = true
value.layer.cornerRadius = 150 * 0.05
// 그림자
value.shadowColor = UIColor.black
return value
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
//UILabel를 view에 추가
self.view.addSubview(noB_Label)
//UITextView를 view에 추가
self.view.addSubview(noB_TextView)
//화면 중앙 배치
noB_Label.snp.makeConstraints { (constraint) in
constraint.center.equalTo(self.view)
}
let nH : CGFloat = noB_Label.frame.height
noB_TextView.snp.makeConstraints { (constraint) in
//noB_TextView의 top 위치를 noB_Label의 bottom dp margine 50을 설정
constraint.top.equalTo(noB_Label.snp_bottomMargin).offset(50)
//noB_TextView의 좌/우측 기준을 noB_Label보다 +/-50으로 설정
constraint.left.equalTo(noB_Label.snp_leftMargin).offset(-50)
constraint.right.equalTo(noB_Label.snp_rightMargin).offset(50)
//noB_TextView의 넓이를 noB_Label의 넓이와 동일 하도록.
/** constraint.width.equalTo(noB_Label) **/
//noB_TextView의 높이를 100으로 설정
constraint.height.equalTo(nH)
}
//둥근 모서리
noB_TextView.layer.cornerRadius = nH * 0.05
}
override func viewWillAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewWillAppear(animated)
}
}
'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [iOS] - UILabel (0) | 2020.08.02 |
|---|---|
| [iOS] - SnapKit : Layout 정리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - CocoaPods(코코아팟), Xcode의 Library 관리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - Storyboard와 SwiftUI 없이 Project 만들기 (0) | 2020.07.31 |
글
[iOS] - UILabel
- UILabel 내용 정리
- Snapkit으로 ui-component들을 배치합니다.
- SnapKit의 기본 지식은 2020/08/01 - [iOS] - iOS - SnapKit : Layout 정리를 참고.
import Foundation
import SnapKit
class TestUILabelVC: UIViewController {
lazy var noB_Label : UILabel = {
// Label 생성 => 가로 300 , 세로 300
let lbl : UILabel = UILabel (frame : CGRect (x: 0 , y: 0 , width: 300 , height: 300 ))
lbl.backgroundColor = UIColor.black
lbl.text = "No.B.Rain 노비의 문서"
lbl.textColor = UIColor.yellow
// Text 정렬 (중앙)
lbl.textAlignment = NSTextAlignment.center
// 둥근 모서리 => 둥근 모서리는 컨탠츠 높이의 5%가 가장 적당하고 이쁨(개인적으로..)
lbl.layer.masksToBounds = true
lbl.layer.cornerRadius = 150 * 0.05
// 그림자
lbl.shadowColor = UIColor.black
return lbl
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
//UILabel 화면에 추가
self.view.addSubview(noB_Label)
//화면 중앙 배치
noB_Label.snp.makeConstraints { (constraint) in
constraint.center.equalTo(self.view)
}
}
}

'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [iOS] - UITextView (0) | 2020.08.02 |
|---|---|
| [iOS] - SnapKit : Layout 정리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - CocoaPods(코코아팟), Xcode의 Library 관리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - Storyboard와 SwiftUI 없이 Project 만들기 (0) | 2020.07.31 |
글
[iOS] - SnapKit : Layout 정리
● Subject : Auto Layout apply using the Snapkit library
- To do
- SnapKit을 사용하여 아주 간단한 화면 배치를 해볼 것입니다.
- Safe Area 영역 구성
- SnapKit 화면 구성 팁
- SnapKit - 기본 구성
import UIKit
import SnapKit
class MyMainView: UIViewController {
lazy var myButtonCenter: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(C) ", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.red
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonTop: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(T)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.blue
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonLeft: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(L)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.green
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonRight: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(R)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.yellow
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonBottom: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(B)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.cyan
return btn
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
view.addSubview(myButtonCenter)
view.addSubview(myButtonTop)
view.addSubview(myButtonBottom)
view.addSubview(myButtonLeft)
view.addSubview(myButtonRight)
myButtonCenter.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.center.equalTo(view)
}
myButtonTop.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.top.centerX.equalTo(view)
}
myButtonBottom.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.bottom.centerX.equalTo(view)
}
myButtonLeft.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.left.centerY.equalTo(view)
}
myButtonRight.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.right.centerY.equalTo(view)
}
}
}- 실행화면.
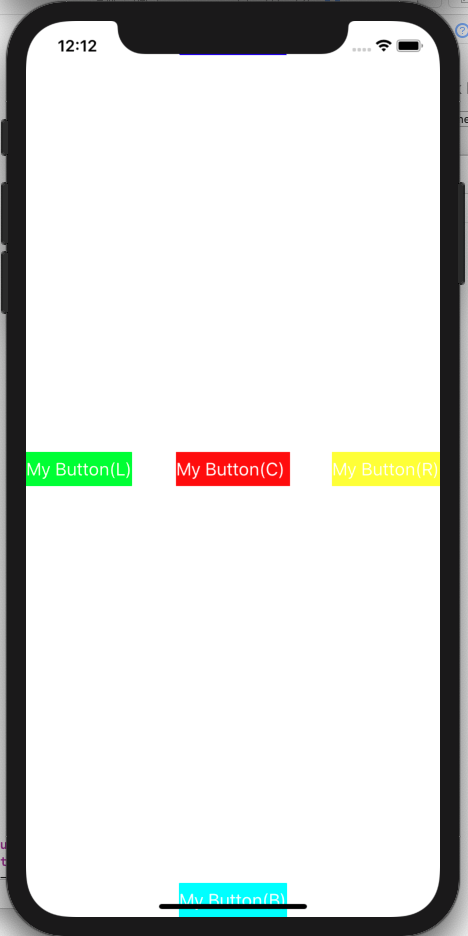
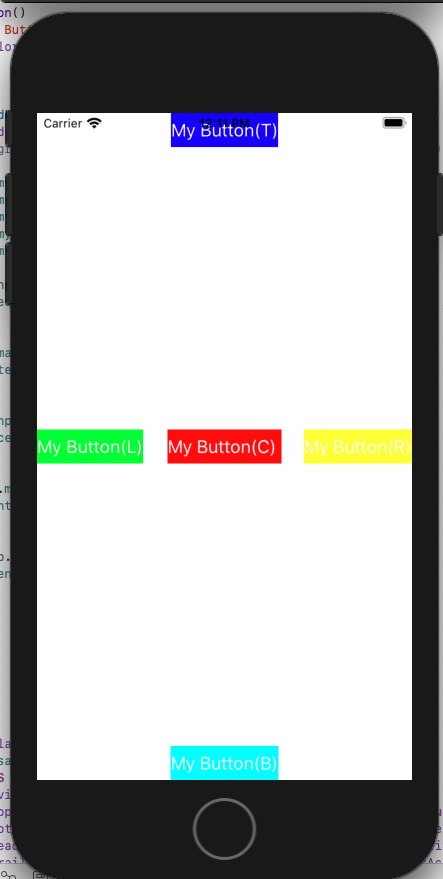
- SnapKit - safe area 영역
import UIKit
import SnapKit
import Foundation
class MyMainView: UIViewController {
let safetyArea: UIView = {
let v = UIView()
v.backgroundColor = .black
return v
}()
lazy var myButtonCenter: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(C) ", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.red
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonTop: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(T)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.blue
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonLeft: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(L)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.green
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonRight: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(R)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.yellow
return btn
}()
lazy var myButtonBottom: UIButton = {
let btn = UIButton()
btn.setTitle("My Button(B)", for: .normal)
btn.backgroundColor = UIColor.cyan
return btn
}()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
setBaseView()
setView()
}
func setBaseView(){
safetyArea.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(safetyArea)
if #available(iOS 11, *) {
let guide = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide
safetyArea.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.topAnchor).isActive = true
safetyArea.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.bottomAnchor).isActive = true
safetyArea.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
safetyArea.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
} else {
safetyArea.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: topLayoutGuide.topAnchor).isActive = true
safetyArea.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: bottomLayoutGuide.bottomAnchor).isActive = true
safetyArea.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
safetyArea.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
}
}
func setView() {
safetyArea.addSubview(myButtonCenter)
safetyArea.addSubview(myButtonTop)
safetyArea.addSubview(myButtonBottom)
safetyArea.addSubview(myButtonLeft)
safetyArea.addSubview(myButtonRight)
myButtonCenter.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.center.equalTo(safetyArea)
}
myButtonTop.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.top.centerX.equalTo(safetyArea)
}
myButtonBottom.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.bottom.centerX.equalTo(safetyArea)
}
myButtonLeft.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.left.centerY.equalTo(safetyArea)
}
myButtonRight.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.right.centerY.equalTo(safetyArea)
}
}
}- 실행화면
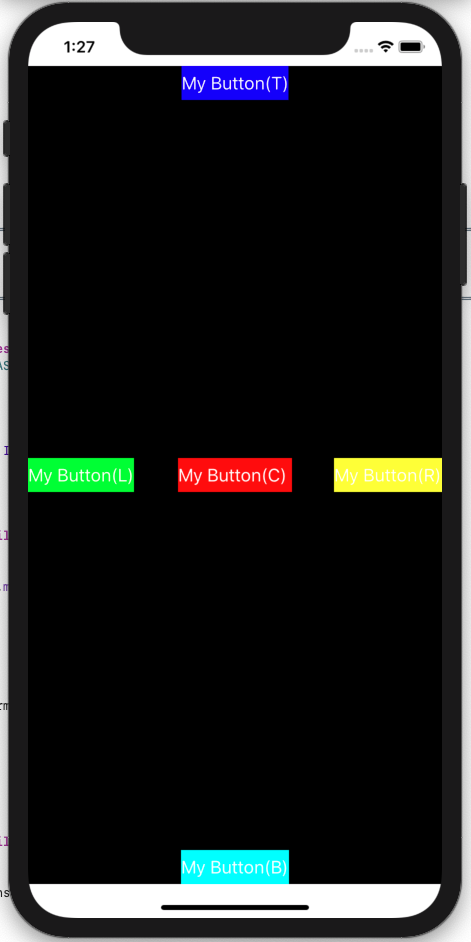

- SnapKit 화면 구성 팁
/*** 화면에 표현할 UILabel 2개 준비 ***/
lazy var box_A: UILabel = {
let lbl = UILabel()
lbl.textColor = .black
lbl.text = "*************************"
lbl.backgroundColor = .blue
lbl.textAlignment = .center
return lbl
}()
lazy var box_B: UILabel = {
let lbl = UILabel()
lbl.textColor = .black
lbl.text = "--------------------"
lbl.backgroundColor = .red
lbl.textAlignment = .center
return lbl
}()
/*** 기준(box_A)에 의해 (box_B)를 크기및 위치 조정 ***/
func test_adjust_size() {
self.view.addSubview(box_A)
self.view.addSubview(box_B)
box_A.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.center.equalTo(self.view)
}
box_B.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.size.equalTo(box_A)
make.top.equalTo(box_A.snp_bottomMargin).offset(20)
make.left.equalTo(box_A)
}
}
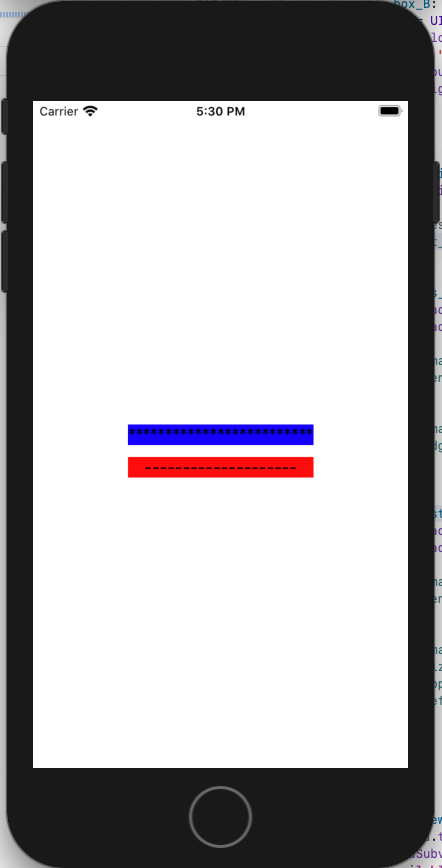
/*** edge test ***/
func test_edges_View() {
self.view.addSubview(box_A)
self.view.addSubview(box_B)
box_A.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.center.equalTo(self.view)
}
box_B.snp.makeConstraints { (make) in
make.edges.equalTo(box_A)
.inset(UIEdgeInsets(top: 10,left: 10,bottom: 10,right: 10))
}
} 
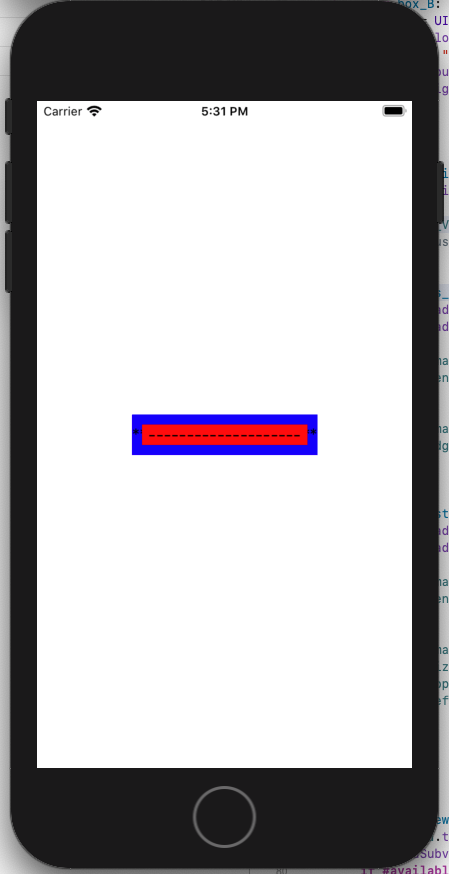
유용한 function
!! snp.updateConstraints : Constraint를 업데이트할 필요가 있을 때
!! snp.remakeConstraints: Constraint를 지우고 다시 설정
'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [iOS] - UITextView (0) | 2020.08.02 |
|---|---|
| [iOS] - UILabel (0) | 2020.08.02 |
| [iOS] - CocoaPods(코코아팟), Xcode의 Library 관리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - Storyboard와 SwiftUI 없이 Project 만들기 (0) | 2020.07.31 |
글
[iOS] - CocoaPods(코코아팟), Xcode의 Library 관리
● 주제 : CocoaPods가 무엇인지 알고, 사용법을 익힙니다.
- 할 일
- CocoaPods 이란?
- Cocoapods 사용법.
- 내용
- CocoaPods 이란? - https://cocoapods.org/ 에 가서 보면 "WHAT IS COCOAPODS"에 간단명료하게 설명을 합니다. CocoaPods는 Swift와 Objective-C Cocoa Project의 dependency를 management 하는 기능을 하며, 아주 많은 앱에서 사용 중이고 project의 확장을 아름답게 도와준다고 자랑..... 하고 있습니다. ㅡ_ㅡ;;; 뭐 덧 붙일 내용이 없네요. ㅎㅎ
- Cocoapods 사용법 - cocoapods 설치
$ sudo gem install cocoapods- Cocoapods 사용법 - 사용
순서
1) "Podfile" 을 만들기 위해 프로젝트 폴더로 이동
2) "Podfile" 생성
3) "Podfile" 편집
4) vi 상의 "Podfile" 파일 내용 및 수정
5) "Podfile" 설치
$ cd "my-prject"
$ pod init
$ vi Podfile
# Uncomment the next line to define a global platform for your project
# platform :ios, '9.0'
target '프로젝트 명' do
# Comment the next line if you don't want to use dynamic frameworks
use_frameworks!
###'아래 부분에 필요한 라이브러리 추가 (SnapKit,AFNetworking,RealmSwift)'
pod 'SnapKit', '~> 5.0.0'
pod 'AFNetworking', '~> 3.0'
pod 'RealmSwift'
###'필요한 라이브러리 추가 끝'
# Pods for 프로젝트 명
target '프로젝트 명' do
inherit! :search_paths
# Pods for testing
end
target '프로젝트 명' do
# Pods for testing
end
end
** Podfile 편집
###'아래 부분에 필요한 라이브러리 추가 (SnapKit,AFNetworking,RealmSwift)'
pod 'SnapKit', '~> 5.0.0'
pod 'AFNetworking', '~> 3.0'
pod 'RealmSwift'
###'필요한 라이브러리 추가 끝'
** Podfile 설치
$ pod install

** Podfile 적용 후 Xcode loading file : "프로젝트명. xcworkspace" 파일로 프로젝트를 열 수 있습니다.

'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [iOS] - UITextView (0) | 2020.08.02 |
|---|---|
| [iOS] - UILabel (0) | 2020.08.02 |
| [iOS] - SnapKit : Layout 정리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - Storyboard와 SwiftUI 없이 Project 만들기 (0) | 2020.07.31 |
글
[iOS] - Storyboard와 SwiftUI 없이 Project 만들기
● 주제 : Storyboard를 사용하지 않고 소스만으로 프로젝트를 만들어 보려 합니다.
- 왜 Storyboard 없이 소스만으로 프로젝트를 만들려고 할까?
- git과 같은 형상관리 툴을 사용해서 협업을 할 때 심심 찬 게 Storyboard의 영역에서 충돌(conflict)이 발생하고, 이를 해결하기 위한 시간적 비용도 많이 소비됩니다.
- 복잡한 Layout을 표현할 때 소스로 구현하면 제약조건(Constraint)을 쉽게 적용하고 추적할 수가 있습니다. 소스로 구현하다 보면, 자연스럽게 ViewController도 재사용을 하게 되고요.
- 할 일
- 프로젝트 만들기
- sceneDelegate 삭제 (프로젝트에 등록된 정보와 소스파일 삭제)
- 새 ViewController 만들기 ("MyRootView.swift" , "MyRootView.xib" 생성과 두 파일과의 연결)
- AppDelegate 수정 (앱의 기본 화면이 될 "MyRootView"와 UINavigationController를 등록)
- 프로젝트 만들기 - 아래 그림과 같이 User Interface의 값은 "Storyboard"로 설정합니다.

- sceneDelegate 등록 정보 삭제 - "Info.plist"의 Application Scene Manifest" 항목 삭제 -> "-" 버튼 눌러서 프로젝트에 등록된 기본 화면 정보를 삭제합니다.

- sceneDelegate 소스 파일 삭제 - 위 내용에 이어서 실제 "sceneDelegate.swift"파일을 삭제합니다.

- 새 ViewController 만들기 : "MyRootView.swift" - 새 파일 만들기 메뉴 경로 "File -> New -> File..."로 이동하여" "Swift File"을 선택하고, "Next"버튼을 누른 후 "MyRootView.swift 2)"처럼 Save as에 MyRootView와 같이 파일명을 입력 후 "Create" 버튼을 누릅니다.


- 새 ViewController - "MyRootView.swift" 파일 작성
//UIKit 추가
import UIKit
import Foundation
//Class 생성과 UIViewController 상속
class MyRootView: UIViewController {
//viewDidLoad 오버라이드
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// 실행시 초록색 화면이 보입니다. (메인화면을 잘 봐꿨는지 확인용.)
self.view.backgroundColor = UIColor(red: 0, green: 1, blue: 0, alpha: 0.3)
}
}
- 새 ViewController 만들기 : "MyRootView.xib" - 새 파일 만들기 메뉴 경로 "File -> New -> File..."로 이동하여" "View"를 선택하고, "Next"버튼을 누른 후 "MyRootView.xib 2)"처럼 Save as에 MyRootView와 같이 파일명을 입력 후 "Create" 버튼을 누릅니다.


- 새 ViewController 만들기 : "MyRootView.xib의 File's Owner의 Custom Class에 MyRootView.swift 연결"


- AppDelegate 수정 - "UISceneSession Lifecycle"의 관련된 내용을 삭제합니다.
- 참고로, SwiftUI는 이전 버전과의 호환성이 없는 문제점이 있습니다. (단지 제 의견이다만,) 시간이 지나고 SwiftUI 가 조금 더 다듬어지고 유연해진다면 SwiftUI는 대중화될 것입니다. 하지만 하위 버전의 호환성을 고려하지 않고 개발하는 경우가 아니면 호환성을 고려해서 SwiftUI를 덜어 내는 것이 정신 건강상 좀 더 좋을 것 같습니다. ^^;
import UIKit
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
return true
}
/** 여기부터 지움... (UISceneSession 관련 내용)
// MARK: UISceneSession Lifecycle
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
configurationForConnecting connectingSceneSession: UISceneSession,
options: UIScene.ConnectionOptions) ->
UISceneConfiguration {
// Called when a new scene session is being created.
// Use this method to select a configuration to
// create the new scene with.
return UISceneConfiguration(name: "Default Configuration", sessionRole: connectingSceneSession.role)
}
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didDiscardSceneSessions sceneSessions: Set<UISceneSession>) {
// Called when the user discards a scene session.
// If any sessions were discarded while the application was not running,
// this will be called shortly after application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions.
// Use this method to release any resources that were specific to the discarded scenes,
// as they will not return.
}
여기까지... (UISceneSession 관련 내용)
*/
}- AppDelegate 수정 - MyRootView와 UINavigationController 등록
import UIKit
import Foundation
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
// rootViewController에 navigation 을 등록할 UIWindow.
var window: UIWindow?
// 화면 이동과 화면 이력을 관리할 UINavigationController 추가.
var navigation : UINavigationController? = nil
// 앱이 시작 할 때 보여 줄 기본 화면 (이름을 MyRootView 로 정함.)
var myRootView : MyRootView!
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
// 아래 내용 작성.
myRootView = MyRootView()
navigation = UINavigationController.init(rootViewController: myRootView)
// 상단 네비게이션바 숨김.
navigation?.setNavigationBarHidden(true,animated: false)
window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
window?.rootViewController = navigation
return true
}
/** 여기부터 지움... (UISceneSession 관련 내용)
// MARK: UISceneSession Lifecycle
- 결과 화면 - 위 MyRootView의 배경색 설정이 적용된 ViewController로 적용이 되어서 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.

*^^* 여기까지 읽어주신 독자님께 감사드립니다. iOS 개발을 배워 나가며 쓰는 글입니다. 글의 내용 중 틀린 내용이 있거나 부족한 점 있다면 귀뜸 부탁드립니다.
다음 글은 Snapkit의 project 등록과 사용법 공부해 보겠습니다.
'iOS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [iOS] - UITextView (0) | 2020.08.02 |
|---|---|
| [iOS] - UILabel (0) | 2020.08.02 |
| [iOS] - SnapKit : Layout 정리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
| [iOS] - CocoaPods(코코아팟), Xcode의 Library 관리 (0) | 2020.08.01 |
